![]()
T1FS
In this section, we are going to see how T1FSs can be defined using the T1FS class. A T1FS is defined by its Membership Function (MF). So first we need to know functions, which can be used as MFs. The list of membership functions provided with the PyIT2FLS is presented below:
List of membership functions that can be used as MF functions
| Membership function | Description | List of parameters |
|---|---|---|
| zero_mf | All zero membership function | None |
| singleton_mf | Singleton membership function | Singleton’s center and height |
| const_mf | Constant membership function | Constant membership function’s height |
| tri_mf | Triangular membership function | The left end, center, right end, and height of the triangular membership function |
| ltri_mf | Left triangular membership function | The left end, center, and height of the triangular membership function |
| rtri_mf | Right triangular membership function | The right end, center, and height of the triangular membership function |
| trapezoid_mf | Trapezoidal membership function | The left end, left center, right center, right end, and height of the trapezoidal membership function |
| gaussian_mf | Gaussian membership function | The center, standard deviation, and height of the gaussian membership function |
| elliptic_mf | Elliptic membership function | The center, width, exponent, and height of the elliptic membership fuction |
| semi_elliptic_mf | Semi-elliptic membership function | The center, width, and the height of the semi-elliptic membership function |
| gbell_mf | Generalized bell shaped membership function | Base on the standard formula, a, b, c, and the height of the generalized bell shaped membership function |
It must be noticed that the parameters of the introduced functions are passed as a list with items mentioned, respectively.
Definition of a membership function in PyIT2FLS
The membership functions introduced in previous section are defined as below:
def membership_function_name(x, params):
# Some calculations ...
return membership_degree
This template can be used by users to define their own new membership functions. It is recommended to use Numpy based mathematic functions for defining new membership functions. The first input of the membership function is a numpy array including some points of the universe of discourse, so the output also must be a numpy array with the same size and shape.
from numpy import linspace
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pyit2fls import zero_mf, singleton_mf, const_mf, tri_mf, ltri_mf, rtri_mf, \
trapezoid_mf, gaussian_mf
domain = linspace(0., 1., 1001)
zero = zero_mf(domain)
singleton = singleton_mf(domain, [0.5, 1.])
const = const_mf(domain, [1.])
tri = tri_mf(domain, [0., 0.5, 1., 1.])
ltri = ltri_mf(domain, [0.5, 1., 1.])
rtri = rtri_mf(domain, [0.5, 0., 1.])
trapezoid = trapezoid_mf(domain, [0., 0.25, 0.75, 1., 1.])
gaussian = gaussian_mf(domain, [0.5, 0.1, 1.])
plt.figure()
plt.plot(domain, zero, label="All zero MF")
plt.plot(domain, const, label="Const MF")
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("Domain")
plt.ylabel("Membership function")
plt.show()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(domain, singleton, label="Singleton MF")
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("Domain")
plt.ylabel("Membership function")
plt.show()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(domain, tri, label="Triangular MF")
plt.plot(domain, ltri, label="Left triangular MF")
plt.plot(domain, rtri, label="Right triangular MF")
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("Domain")
plt.ylabel("Membership function")
plt.show()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(domain, trapezoid, label="Trapezoid MF")
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("Domain")
plt.ylabel("Membership function")
plt.show()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(domain, gaussian, label="Gaussian MF")
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("Domain")
plt.ylabel("Membership function")
plt.show()
T1FS Class
The T1FS class is designed for defining Type 1 Fuzzy Sets. It’s constructor function has three parameters, which are described below:
- domain: Universe of discourse is defined by setting the domain parameter.
- mf: The membership function of the T1FS. The mf must be among the membership functions provided by the PyIT2FLS or a self defined membership function with the introduced structure.
- params: Parameters of the given membership function.
Defuzzification of the T1FSs
Defuzzification of a T1FS is done using the defuzzify function of the class. The only parameter of this function is method of type string. The default value of the parameter is CoG, which indicates the center of gravity defuzzification method. At the moment only center of gravity defuzzification method is implemented but in the near future other methods will be added, too.
Plotting the T1FSs
For plotting the defined T1FSs, the plot function from the T1FS class can be used. This function has three inputs with None default values. The three inputs are title, legend_text, and filename. If the user wants to have a plot with costum title and legend, these two inputs can be set. Also, if the filename parameter is given, then the plot would be saved with the given file name.
Plotting multiple T1FSs together
If there are many sets which we would like to plot them together, we can use the T1FS_plot function from PyIT2FLS. The inputs of this function, after an arbitrary number of T1FSs, are like the intorduced plot function. It means that there are three title, legend_text, and filename parameters with the None default values.
Examples
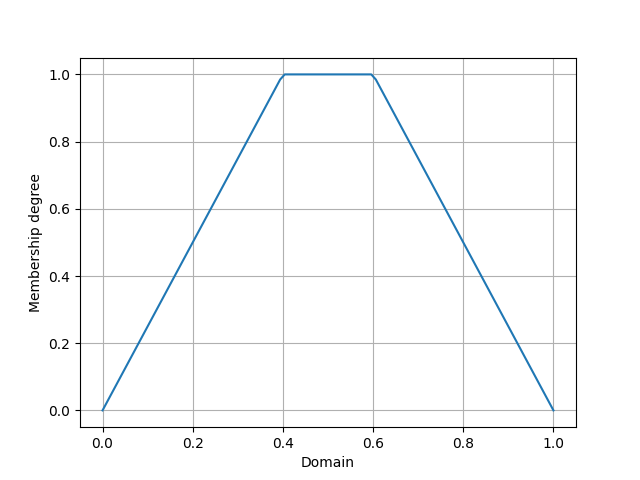
In this section, some examples of defining T1FSs are provided. The first example is after defining a T1FS with trapezoidal MF:
from pyit2fls import T1FS, trapezoid_mf
from numpy import linspace
domain = linspace(0., 1., 100)
mySet = T1FS(domain, trapezoid_mf, [0, 0.4, 0.6, 1., 1.])
mySet.plot()
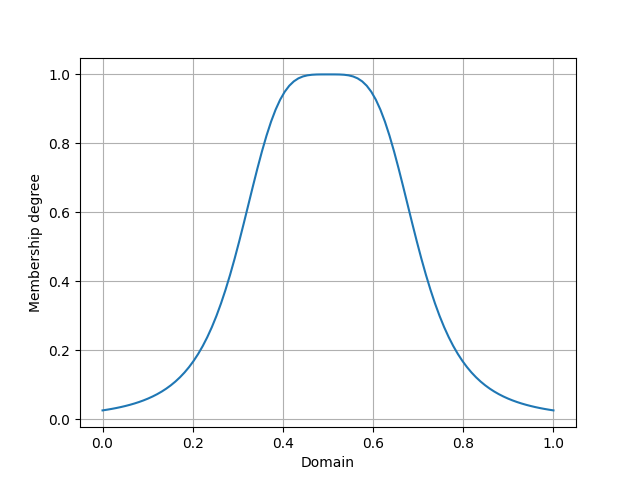
As it is said before, five parameters are needed for defining a trapezoidal membership function. The first four parameters indicate the left end, left center, right center, and right end of the trapezoidal membership function. The last parameter is the height of the membership function which must lay in the interval [0, 1]. The output plot for given parameters and defined universe of discourse would be as below:
In the second example we are going to define three Gaussian T1FSs, and plot them all together.
from pyit2fls import T1FS, gaussian_mf, T1FS_plot
from numpy import linspace
domain = linspace(0., 1., 100)
Small = T1FS(domain, gaussian_mf, [0, 0.15, 1.])
Medium = T1FS(domain, gaussian_mf, [0.5, 0.15, 1.])
Large = T1FS(domain, gaussian_mf, [1., 0.15, 1.])
T1FS_plot(Small, Medium, Large, legends=["Small", "Medium", "large"])
The output plot for this example is represented as below:

Defining a new membership function
In this example we are going to define a new membership function and use it in defining an T1FS. Let’s assume that we are going to define the generalized bell shaped membership function, which has the formula below:
from numpy import abs as npabs
from numpy import linspace
from pyit2fls import T1FS
def gbell_mf(x, params):
return params[3] / (1 + npabs((x - params[2]) / params[0]) ** (2 * params[1]))
domain = linspace(0., 1., 100)
mySet = T1FS(domain, gbell_mf, [0.2, 2., 0.5, 1.])
mySet.plot()
The output plot for this example is represented as below: